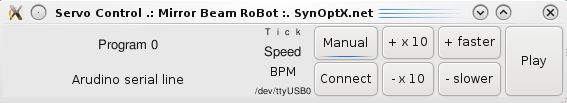
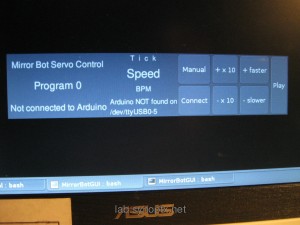
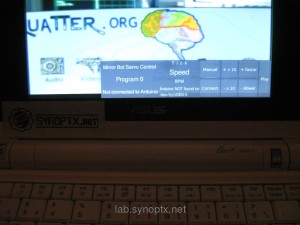
Software Remote Control – Python GTk Servo Control
The software interface is a gtk-python program, which controls the movements by keyboard and graphical user interface.
We use this during live visual performances on a Asus EEE netbook, which is also running as a preview screen for the video mixer output.
There are 9 automatic programs to move the projections in different patterns across the wall.
9 automatic, BPM syncronized mirror movent programs
Program Types:
- Scanner – up down movements in 5° or 10° steps, crossover and following
- Hotspots jumping: various pattern between the 2x 6 hotspots: crossover and following,..
The intervals of the movements can be changed to match to the beat of the music in BPM. In manual mode, the mirrors can be moved directly by knobs, – so it can be used just as a live instrument.
This program is focused all the time and receives keyboard inputs. Often we move the buttons out of the screen to see only the display with interesting values (current mirror positions, program,BPM) of the bots.
The keyboard inputs are sent to the Arduino practically directly over serial by the python GUI. Button click events in the interface also send one char over serial line.
The standard Arduino firmware is limited: it can only receive one char at a time, so for receiving a string of multiple letters you need to implement a loop and wait for a terminating string. For this reason the first version of this software could sent only “+” and “-” to change the speed, but not a complete new value (like “180” BPM) 🙂
Keyboard Shortcuts:
- 0-9 : select program
- “s” : start / stop
- + : faster (+1 BPM)
- – : slower(-1 BPM)
- x : manual mode on/off
The python GUI also reveives strings over serial from the Arduino and extracts the interesting values to display and then refreshs the text fields.
The data format sent by the Arduino is very short and simple, because the serial line is just fast enough to transfer:
- short program descriptions (20 chars) – on program change events
- current speed – every 100-200ms
- beat tick – on timeout
Sending longer strings blocks the Arduino and it will not respond to serial input or loose some commands.
Luckily sending and receiving contemporary works just fast enough and also python/Gtk handles input and output easily without threading.
btw: do not use to many (long) strings in Arduino or the RAM and flash memory is full soon, but its not that bad (specially with the 328) – this software, uses less than half the flash memory and ca. 1/4 of the RAM. (must check..)