Mirror Bots .: moving visuals projections – standalone & Linux GUI controller
This is a robotic system to move VJmix projections all over the walls.
Video: MirrotBot in Action Köpi, Berlin 11.2008

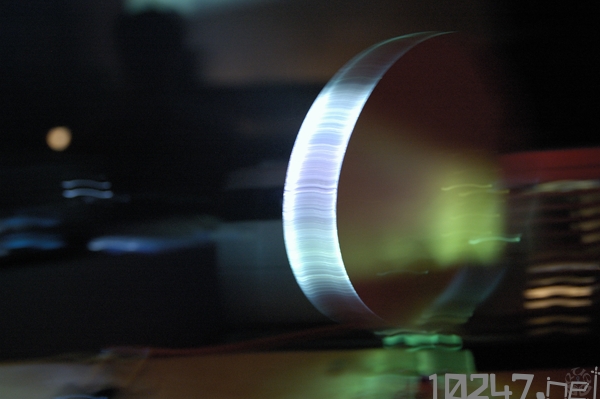
Beamer projection reflection on mirror
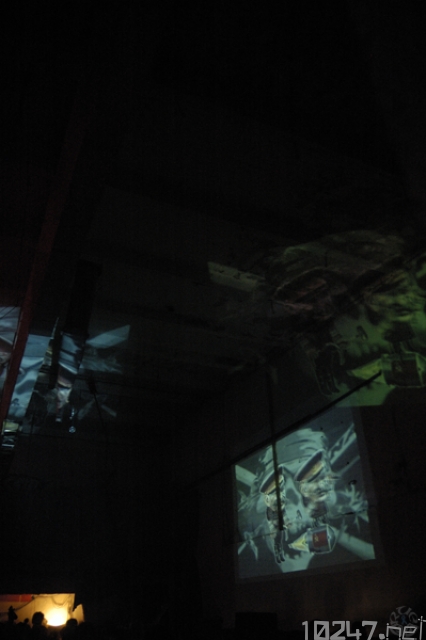
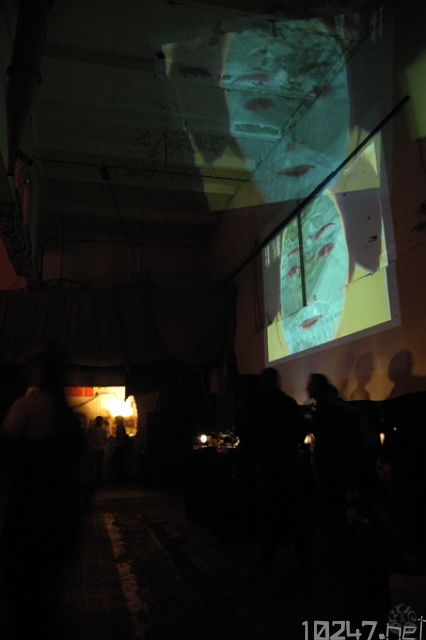
Mirrors are mounted on servo motors to rotate them in front of dia projectors or beamers. This way, the projections are moved across the walls and the ceiling of the room.
A microcontroller system, connected to a netbook, is used to control the mirror-servo-unit movements.
“Hotspots” are defined to project on the best spots on the walls of the location and create an impressive light show of moving rays and projections on all walls and screens.

1.prototype live action with diaprojector & beamer
This system can be installed in rooms of any size.
It is required to use projection glass or there are double projections and very unsharpened results. The beamers must be powerful to show bright images also on the must distant walls. In big rooms, the projections are really big, so the 2 video mixes can work together as moving textures or moving characters.
The proof-of-concept system was first used by Headsquatter Live Visuals in Berlin @MIKZ – Suchtfaktor – 27.09.2008 with great success and continuously enhanced and tested live.
Hardware
We use a common, programmable input/output hardware controller to trigger motors: Arduino Dicemilia.

1.prototype live action -- only left dia is mirrored
Two Mirrors are mounted on servos to move them in front of two video beamers. This first version can move 2 projections with 2 mirrors on one horizontal axis between 40° and 130° – ca. It creates distorted projections depending on the current angle, but works very well with various kinds of video mixes. High contrast images and vectorial animations work specially good. By positioning two projections besides each other there appear many interesting possibilities.
Combined with fog machines the rays become visible and the moving beams look like a laser show with real videos.
The servo-mirror movements are synchronized to the beat of the music and many programs can be selected, to move the projections in various patterns.

VJ Live Mix Box: Wiimote - VJ mixer - Arduino Servo Control - Mirror (+ eeePC 🙂 ) - Linux Netbook
Software
This MirrorBot is controlled by a linux netbook over serial console via USB cable. The prototype is remote-controlled by a simple software command line. Various keyboard key presses change program, speed, play/pause mode of the attached servo control box. This works quite good during live visuals mixes, with a mini terminal window in front of a TVtime preview screen of the video mixer.
Pictures by Rue23 in MIKZ 27.09.2008 – Suchtfaktor Party ::
more Pix @